25% as a decimal is 0.25, and since we subtract 25% we use (1 - 0.25)=0.75.
The price of the items after discount is $248.50*0.75 = $186.38
The sales tax (5% = 0.05) is added on, so we multiply by (1 + 0.05) = 1.05
$186.375*1.05 = $195.699 = $195.70
Answer: 2/8.
Step-by-step explanation:
When we have this type of problem, the usual way to solve them is trying with known types of sequences.
I will start with the arithmetic sequence, where the difference between any two consecutive terms is a constant. And if we call this difference as D, we will have the recursive relation:
Aₙ = Aₙ₋₁ + D
To check if this sequence is an arithmetic sequence, we can take the first two terms and see the difference:
(5/8 - 3/4) = (5/8 - 6/8) = -1/8.
Now let's do the same, but with the second and third terms:
(1/2 - 5/8) = (4/8 - 5/8) = -1/8
The difference is the same, -1/8.
Now we can use the recursive relationship above and the last given term of the sequence to find the next one:
A₅ = A₄ + (-1/8)
A₅ = 3/8 - 1/8 = 2/8
Then the next fraction in the sequence was 2/8.
Answer:
1)38.5
2)39
Step-by-step explanation:
median: put the numbers smallest to biggest the cross out the number from both sides one by one until you get to the middle if there are two numbers in the middle the add them and divide it by 2
mean: add them all up and then divide by how many numbers there are in total
Answer:
a. Type I error because the principal rejected the null hypothesis when it was true.
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given that principal of a school believed that his students scored better than the national average. For this principal collected a simple random sample of student SAT scores in math. The sample data collected had a mean student SAT score higher than 550 and the calculated P-value indicated that the null hypothesis should be rejected which means;
Null Hypothesis,  :
:  = 550 {means school's students' SAT scores is the same as the national mean score of 550}
= 550 {means school's students' SAT scores is the same as the national mean score of 550}
Alternate Hypothesis, 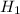 :
:  > 550 {means school's students' SAT scores is higher than the national mean score of 550}
> 550 {means school's students' SAT scores is higher than the national mean score of 550}
But, in fact, the true population mean of that school's students' SAT scores is the same as the national mean score and P-value indicates that the null hypothesis should be rejected.
Hence error has been occurred.
Type I error states that Probability of rejecting null hypothesis given the fact that  is true and this is the case of our question as Principal had rejected the null hypothesis based on p-value but in actual
is true and this is the case of our question as Principal had rejected the null hypothesis based on p-value but in actual  was true.
was true.