Answer:
Type I error will be Rejecting the null hypothesis that the average diameter of needles is 1.65 mm and assume that the average diameter of needles is different from 1.65 mm but the fact is that the null hypothesis was true that the average diameter of needles is 1.65 mm.
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given that a manufacturing process is producing hypodermic needles that will be used for blood donations. These needles need to have a diameter of 1.65 mm—too big and they would hurt the donor (even more than usual), too small and they would rupture the red blood cells, rendering the donated blood useless.
So, Null Hypothesis,  :
:  = 1.65 mm
= 1.65 mm
Alternate Hypothesis, 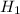 :
:  1.65 mm
1.65 mm
Also, the most recent random sample of 35 needles have an average diameter of 1.64 mm and a standard deviation of 0.07 mm.
Now, <u>Type I error Type I error states that </u>: Probability of rejecting null hypothesis given the fact that null hypothesis was true. It is the the probability of rejecting a true hypothesis.
<em>So, in our question Type I error will be Rejecting the null hypothesis that the average diameter of needles is 1.65 mm and assume that the average diameter of needles is different from 1.65 mm but the fact is that the null hypothesis was true that the average diameter of needles is 1.65 mm.</em>