Answer:
(a) C: 0.0465 ; reject the null hypothesis
(b) B: 0.3409 ; fail to reject the null hypothesis
Step-by-step explanation:
Firstly, the decision rule based on P-value to reject the null hypothesis or fail to reject the null hypothesis is given by;
- If the P-value of test statistics is less than the level of significance, then we have sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis.
- If the P-value of test statistics is more than the level of significance, then we have insufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis due to which we fail to reject our null hypothesis.
(a) Now, we are given alternate hypothesis, 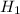 : p < 3/5
: p < 3/5
Also, z test statistics is -1.68. Since this is a left tailed test, so P-value is given by;
P-value = P(Z < -1.68) = 1 - P(Z  1.68)
1.68)
= 1 - 0.95352 = <u>0.0465</u>
Since, the P-value of test statistics is less than the level of significance as 0.0465 < 0.05, so we have sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis due to which <u>we reject the null hypothesis.</u>
(b) Now, we are given alternate hypothesis, 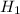 : p > 0.383
: p > 0.383
Also, z test statistics is 0.41. Since this is a right tailed test, so P-value is given by;
P-value = P(Z > 0.41) = 1 - P(Z  0.41)
0.41)
= 1 - 0.6591 = <u>0.3409</u>
Since, the P-value of test statistics is more than the level of significance as 0.3409 > 0.05, so we have insufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis due to which <u>we fail to reject the null hypothesis.</u>