Answer:
Test statistics = 2.29
P-value = 0.01101
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given that a survey conducted five years ago by the health center at a university showed that 18% of the students smoked at the time. This year a new survey was conducted on a random sample of 200 students from this university, and it was found that 50 of them smoke.
Let Null Hypothesis,  : p = 0.18 {means that the percentage of students who smoke has remained same at 18% over the last five years}
: p = 0.18 {means that the percentage of students who smoke has remained same at 18% over the last five years}
Alternate Hypothesis, 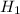 : p > 0.18 { means that the percentage of students who smoke has increased over the last five years}
: p > 0.18 { means that the percentage of students who smoke has increased over the last five years}
The test statistics used here will be ;
T.S. =  ~ N(0,1)
~ N(0,1)
where,  = sample proportion of students = 50/200 = 0.25
= sample proportion of students = 50/200 = 0.25
n = sample size = 200
So, test statistics = 
= 2.29
Now, P-value is given by = P(Z > 2.29) = 1 - P(Z <= 2.29)
= 1 - 0.98899 = 0.01101 or 1.101 %
Therefore, P-value of the test is 0.01101 .
Answer:
Because 8 Percent is not very much speed
8%=0.08
Step-by-step explanation:
Hope this helps!
Answer:
By itself: 32 <u><</u> 17+c
Solved: 15 <u><</u> c
If wanted it to be solved:
32 <u><</u> 17 + c
-17 -17
15 <u><</u> c
Your answer is D. 36 - 8i
<em>I'm only a few Brainliests away from ranking up, so one would be much appreciated. Thank you, and good luck!</em>
Five.
I need some extra characters here.